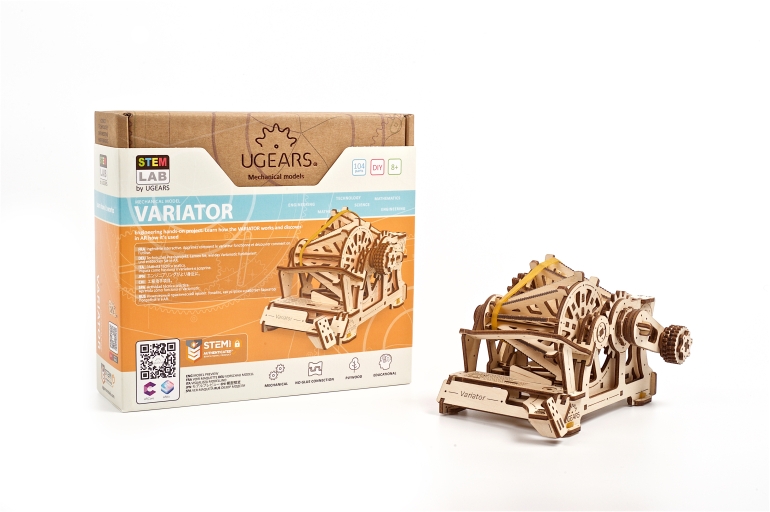
STEM Lab Variator
- Description
- Reviews
- Specifications
Assemble it and discover the principle of working of the Variator.
- The model kit comes with a QR-code that will forward you to the learning guide about the mechanism, the principal of its working, the main characteristics, formulas, and interesting assignments.
- Dive into augmented reality and look at how the random generator works. Interact with the model via a special AR application from Ugears
Find out about the Variator
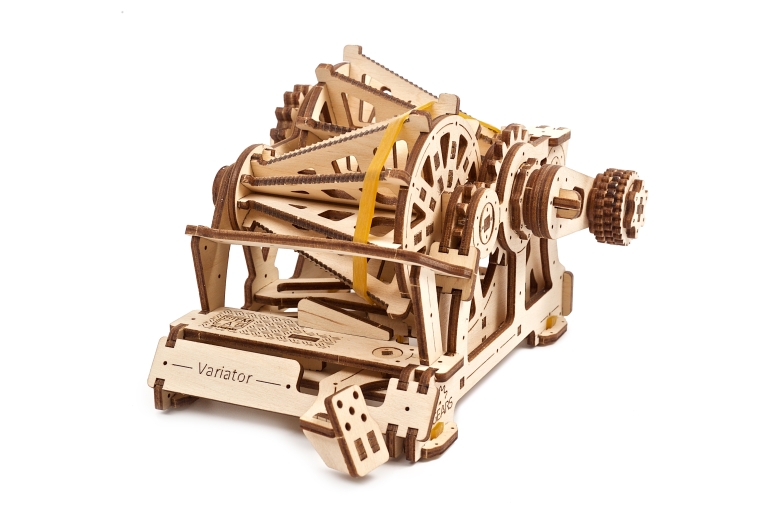
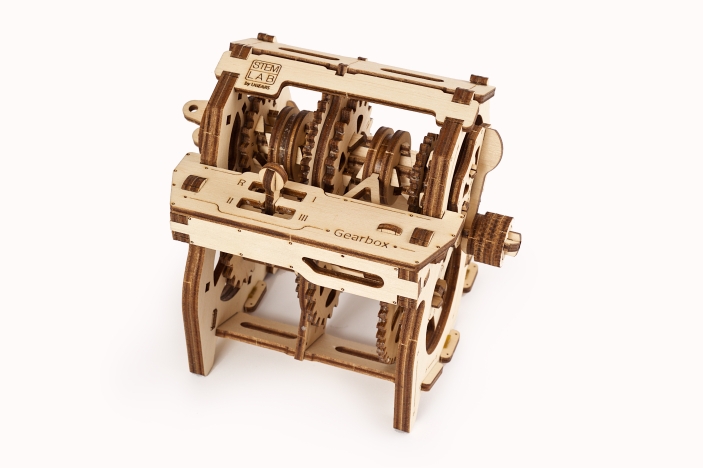
The Variator is a device that transfers and adjusts the engine torque by changing the ratio of gears. Gear ratio can change automatically, manually or within a pre-set program. The term most drivers and automobile enthusiasts are more accustomed with is Continuously Variable Transmission, or CVT. With the Ugears Variator model of the STEM lab collection you can learn and comprehend one of the most important parts of a car without soiling your hands in machine oil!
When and who invented it:
The roots of the modern car CVT go back to 1879 when an American entrepreneur and a pioneer of the automobile industry Milton Othello Reeves invented a device for use in sawmilling that he then called a variable-speed transmission. Later he began fitting this transmission to his cars. The Reeves CVT was also used by several other manufacturers.
Usage:
The CVT is used in mechanisms, in which a continuous range of gear ratios must be changed seamlessly: cars, motor scooters, snowmobiles, quadracycles, conveyors, metal-cutting machines, etc. To have a better idea about how it is used in different types of equipment, try the AR application that comes with the Ugears STEM model.
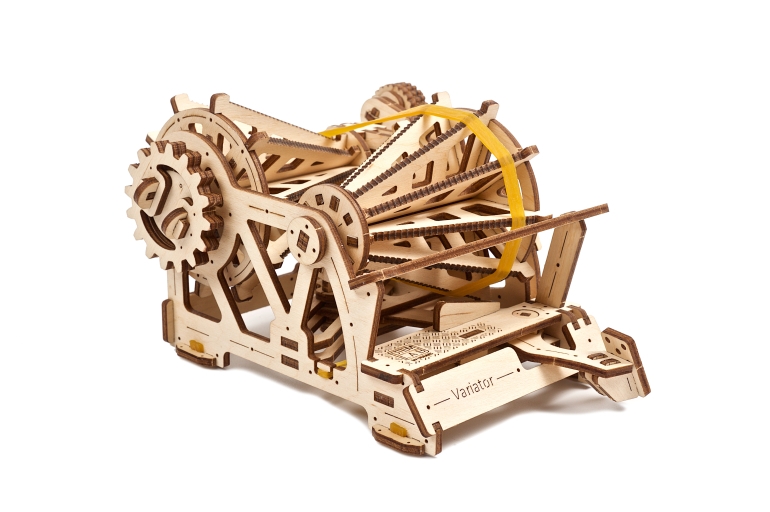
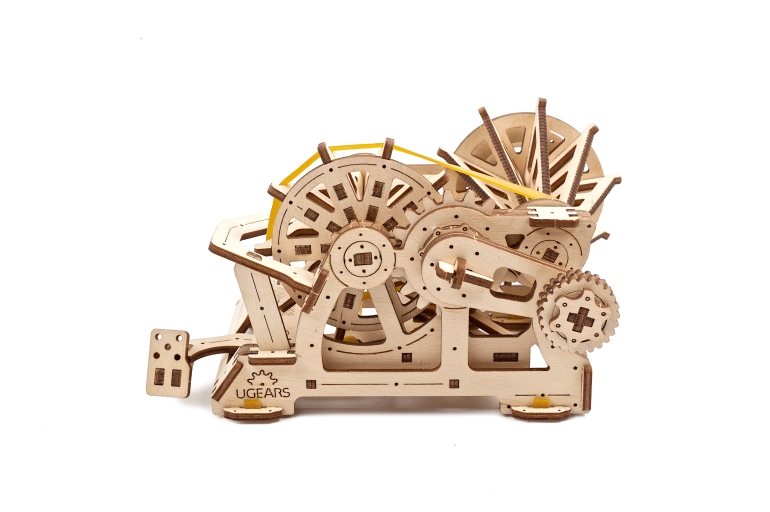
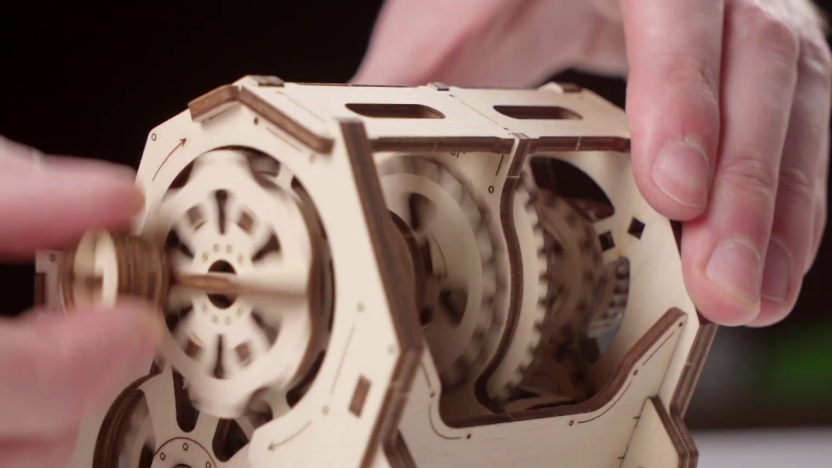
The Variator’s design and how it works
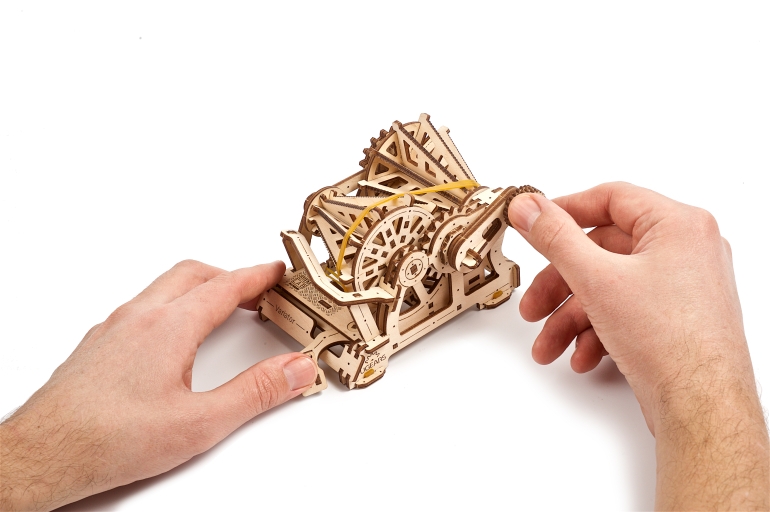
The Mechanical Variator of the Ugears STEM lab collection is a fully functional wooden replica of a Belt-driven Friction Cone CVT. The Cone CVT varies the drive ratio by moving a wheel or belt up and down the axis of conical roller. In the Ugears Variator model, the belt, powered manually via the reducer, transfers the rotation to the driven cone pulleys. Use the transmission fork to change gears and observe how the speed of the driven cone pulley drops or rises while the drive cone pulley’s speed remains the same. Due to the open design of the model, you will be able to see the whole process.